Introduction To Smart AMS IOT

- Introduction to Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled Smart Agriculture monitoring.
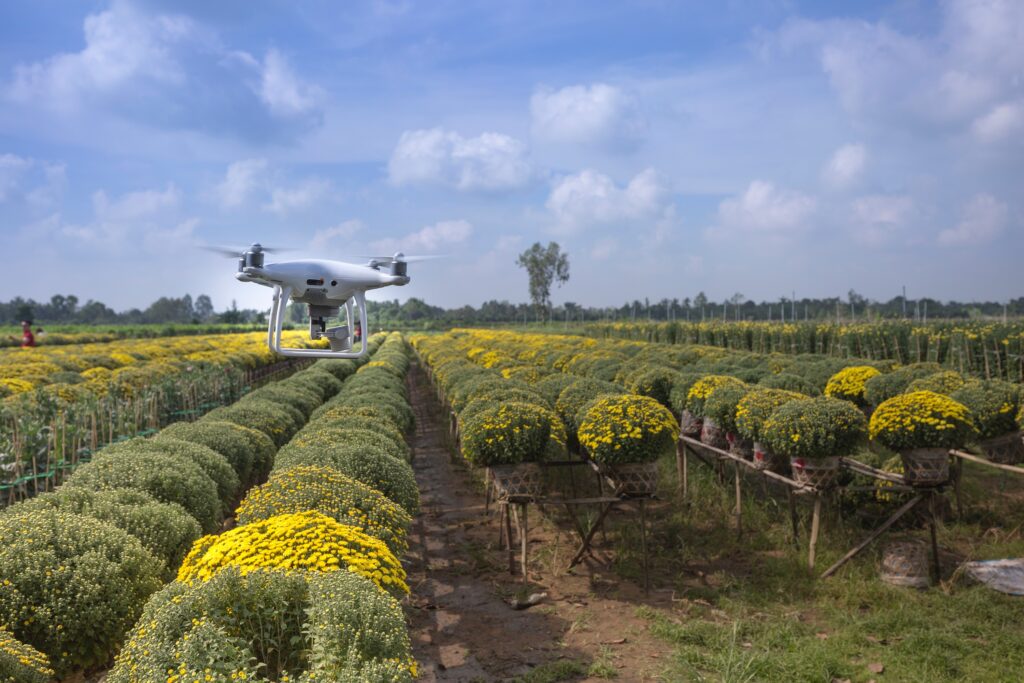
IoT based Smart Agriculture Monitoring is the integration of the technology of internet of things (IoT) with agriculture for better crop and animal husbandry processes. The concept behind precision agriculture is the use of sensor technology, data analysis, and process automation for better monitoring and controlling of different farming activities
- Importance of Intelligent Monitoring in Smart Agriculture.
Smart Agriculture Monitoring” is essential for maximizing resource use, increasing the yield and sustained production. It empowers farmers with data-driven decision making, cost reduction, and lower environmental footprints, tackling the global issues like Food Security and Climate Change.
- Purpose
The purpose behind writing this blog is to present a well-structured brief on IoT-enabled Smart Agriculture Monitoring explaining the architecture, advantages, use cases, hindrances, instances, opportunities, trends, along with much more!

The parts of IoT-based agricultural monitoring.
A. Sensors and Data Collection
Vital data on the environmental conditions is collected through sensors such as soil moisture and weather sensors. Different sensors are used for measuring different farm-related parameters.
B. Data Processing and Analysis
It’s sent off for further processing. Then data analytics tools use these findings in order to generate actionable insights for farmers to help them to make better decisions in regards to their crop yield.
C. Control and Automation
Automatic actions such as tweaking irrigation and running machines are the result of actuators and algorithms driven by data analysis.
D. Communication Infrastructure
With the help of wireless connectivity and IoT protocols data from sensors, computing devices to customers flows smoothly.
Key Features and Benefits
A. Real-time Monitoring
IoT enabled systems provide real time information about field condition and enable quick response to the situations.
B. Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture optimizes resource utilization to minimize the use of resources such as water, fertilizers, pesticides and fuel leading to better crop yield and quality.
C. Resource Optimization
Through efficient irrigation, fertilization, and pest-management systems, less natural resources are used and yields grow.
D. Remote Accessibility
With the help of mobiles farmers could keep on eye and control their operation anywhere from remote, this is flexible and easily approachable.
E. Higher crop yield and quality.
Thanks to IoT-based solutions, crops can be cultivated sustainably and economically, and the crop quality can be improved with the help of data-driven decisions.

Uses of IoT for Intelligent Agriculture Monitoring.
A. Crop Management
1. Soil Health Monitoring: Soil moisture, pH and nutrient levels are measured by sensors to optimize fertilizer application and watering techniques.
2. Irrigation Management: Irrigation systems run automated scheduling based on real-time weather and soil updates.
B. Livestock Monitoring
1. Animal Health Tracking: Sensors keep track of important vitals and behaviors, leading to early diagnosis of diseases and improved care.
2. Environmental Conditions for Livestock: Temperature and humidity sensor for ideal living conditions.
C. Weather Forecasting and Alerts
Weather data is combined in IoT systems to give farmers accurate predictions and warnings about dangerous weather conditions.
D. Pest and Disease Detection
Sensors and analytic tools monitor/detect crop pest and disease problems, enabling timely action.
E. Equipment and Machinery Monitoring
The application of IoT devices allows us to track the condition and operating effectiveness of farm machinery, decreasing down time and maintenance outlays.
Challenges and Considerations
A. Data Privacy and Security
It’s also important to protect confidential agricultural information against threat.
b) connectivity problems in rural areas.
Internet access and network coverage aren’t always dependable in areas of agricultural fields.
C. Cost and Scalability
It is not cheap to implement an IoT solution, and scaling up might require larger investment.
D. Integration with Existing Systems
It’s challenging to integrate IoT systems into legacy devices and processes.
E. Environmental Impact
For IoT infrastructures sustainability and energy usage are major factors.

Case Studies
A. Examples of Successful Implementations
Provide evidence of existing real-world implementations of IoT powered Smart Agriculture monitoring and the benefits they have brought.
B. Impact on Agriculture Productivity
Demonstrate the improvements in crop yields as well as resource usage and revenue.
Future Trends and Innovations
Investigate the latest sensor innovations promising even better data in an affordable way. Talk about AI + ML’s role in data analysis and future decision-making. Investigate how to use blockchain applications to add more transparency and traceability to beef meat supply chain. Think about the role IoT could play in eco-conscious agriculture.
Conclusion
Smart Agriculture Monitoring: An outline of IoT Importance Recall the role these systems play in solving agricultural problems. Opportunity to Transform the Agriculture Industry Highlight the future impact of IoT on the ag industry. Incentive for additional Research and Development. Emphasize the imperative of continuous R&D to progress in the domain of IoT-driven Intelligent agricultural Monitoring.



I was more than happy to find this great site. I want to to thank you for ones time for this particularly fantastic read!! I definitely savored every little bit of it and i also have you bookmarked to see new things on your web site.